The popular Black Dashboard design, crafted by Creative-Tim is now available as a coded web app in Flask, the popular Python Web Framework. Using this free admin dashboard, developers might speed up their development based on the fact that the app is provided with a basic set of features:
- UI-ready (the boring manual processing of HTML files and components extraction is already done)
- App Logic: session-based authentication, ORM, database (SQLite, PostgreSQL)
- Deployment scripts: Docker, Gunicorn/Nginx, Waitress
- License MIT - suitable for hobby and commercial products
- Free Support via Github and paid 24/7 Live support via Discord
App Links
In case you are already familiar with Flask feel free to grab the sources and play with the app:
- Flask Black Dashboard - the product page, published by the AppSeed platform
- Flask Black Dashboard - source code, published on Github
- Flask Black Dashboard - LIVE Demo
Black Dashboard Design
Black Dashboard is a beautiful Bootstrap 4 Admin Dashboard with a huge number of components built to fit together and look amazing. If you are looking for a tool to manage and visualize data about your business, this dashboard is the thing for you. It combines colors that are easy on the eye, spacious cards, beautiful typography, and graphics.
This beautiful and free UI-Kit, coded by Creative-Tim agency comes packed with all plugins that you might need inside a project and documentation on how to get started. It is light and easy to use, and also very powerful.
What is Flask
Flask is a lightweight WSGI web application framework. It is designed to make getting started quick and easy, with the ability to scale up to complex applications. It began as a simple wrapper around Werkzeug and Jinja and has become one of the most popular Python web application frameworks.
It is classified as a microframework because it does not require particular tools or libraries. It has no database abstraction layer, form validation, or any other components where pre-existing third-party libraries provide common functions.
Prepare your environment
To build the app, Python3 should be installed properly in the workstation. If you are not sure if Python is properly installed, please open a terminal and type python --version. The full list with dependencies:
- Python3 - the programming language used to code the app
- Git - the popular versioning tool, used to clone the sources from Github
Check Python version:
$ # Check Python version
$ python --version
Python 3.7.2Check GIT command tool:
$ # Check git
$ git --version
$ git version 2.10For more information on how to set up your environment please access the resources listed below:
- How to set up Python
- Setup CentOS for development
- Setup Ubuntu for development
- Setup Windows for development
Code Structure
The boilerplate code is built with a modular structure that follows the recommended pattern used by many open-source projects. The most important files and directories are shown below:
< PROJECT ROOT > # application root folder
|
|--- app/__init__.py # application constructor
|--- app/base/ # base blueprint
|--- app/base/static/assets # Img, CSS, Janascript files
|--- app/base/templates # Jinja2 files (layouts, login pages)
| |---<errors> # Dir - Error pages: 404, 500
| |---<login> # Dir - Login and Registration pages
| |---<site_template> # Dir - Components: footer, sidebar, header
|
|
|--- app/home/ # home blueprint
|--- app/home/templates # Jinja2 files (Pages): index, icons, tables
| |---- index.html # Main dashboard page
| |---- maps.html # Maps page
| |---- profile.html # Profile Page
| |---- tables.html # UI Tables
| |---- icons.html # Ui Icons
|
|--- .env # store env variables
|--- config.py # app configuration profiles: Debug, Production
|
|--- requirements.txt # Requirements for development - SQLite storage
|--- requirements-pgsql.txt # Requirements for production - Pgsql Database
|
|--- run.py # bootstrap the app
|
|-----------------------------Build from sources
As mentioned before, the source code for Flask Black Dashboard is published on Github, under the MIT license. To clone the source code locally, we need to open a terminal and type:
$ # Get the code
$ git clone https://github.com/app-generator/flask-black-dashboard.git
$ cd flask-black-dashboardOnce the sources are downloaded from the Github platform, the next step is to install the app dependencies, using a virtual environment:
$ # Virtualenv creation (Unix based systems)
$ virtualenv --no-site-packages env
$ source env/bin/activate
$
$ # Install modules - SQLite Database
$ pip3 install -r requirements.txtThis step might take a while, and depends on your internet speed (to download the remote packages) and the CPU power of your machine (the packages are compiled locally). If all goes well, we need to update the environment with variables required by the Flask Framework. Please find below the recommended environment setup for all major operating systems:
$ # Set the FLASK_APP environment variable
$ (Unix/Mac) export FLASK_APP=run.py
$ (Windows) set FLASK_APP=run.py
$ (Powershell) $env:FLASK_APP = ".\run.py"
$
$ # Set up the DEBUG environment
$ # (Unix/Mac) export FLASK_ENV=development
$ # (Windows) set FLASK_ENV=development
$ # (Powershell) $env:FLASK_ENV = "development"At this point, the app is prepared to be started successfully using the Flask embedded WSGI server:
$ # Start the application (development mode)
$ # --host=0.0.0.0 - expose the app on all network interfaces (default 127.0.0.1)
$ # --port=5000 - specify the app port (default 5000)
$ flask run --host=0.0.0.0 --port=5000
$
$ # Access the dashboard in browser: http://127.0.0.1:5000/By default, Flask starts the app on port 5000. If another app already uses this port, we can start our Flask admin dashboard on another port using --port input parameter:
$ flask run --port=5777
$
$ # Access the app in browser: http://127.0.0.1:5777/The application will redirect the guest users to the login screen, and the first thing we will see on the screen is the login page. To unlock the private pages and menus, and pass the login, we need to create a new user. Once the user is authenticated, the app unlocks the private pages and menus:
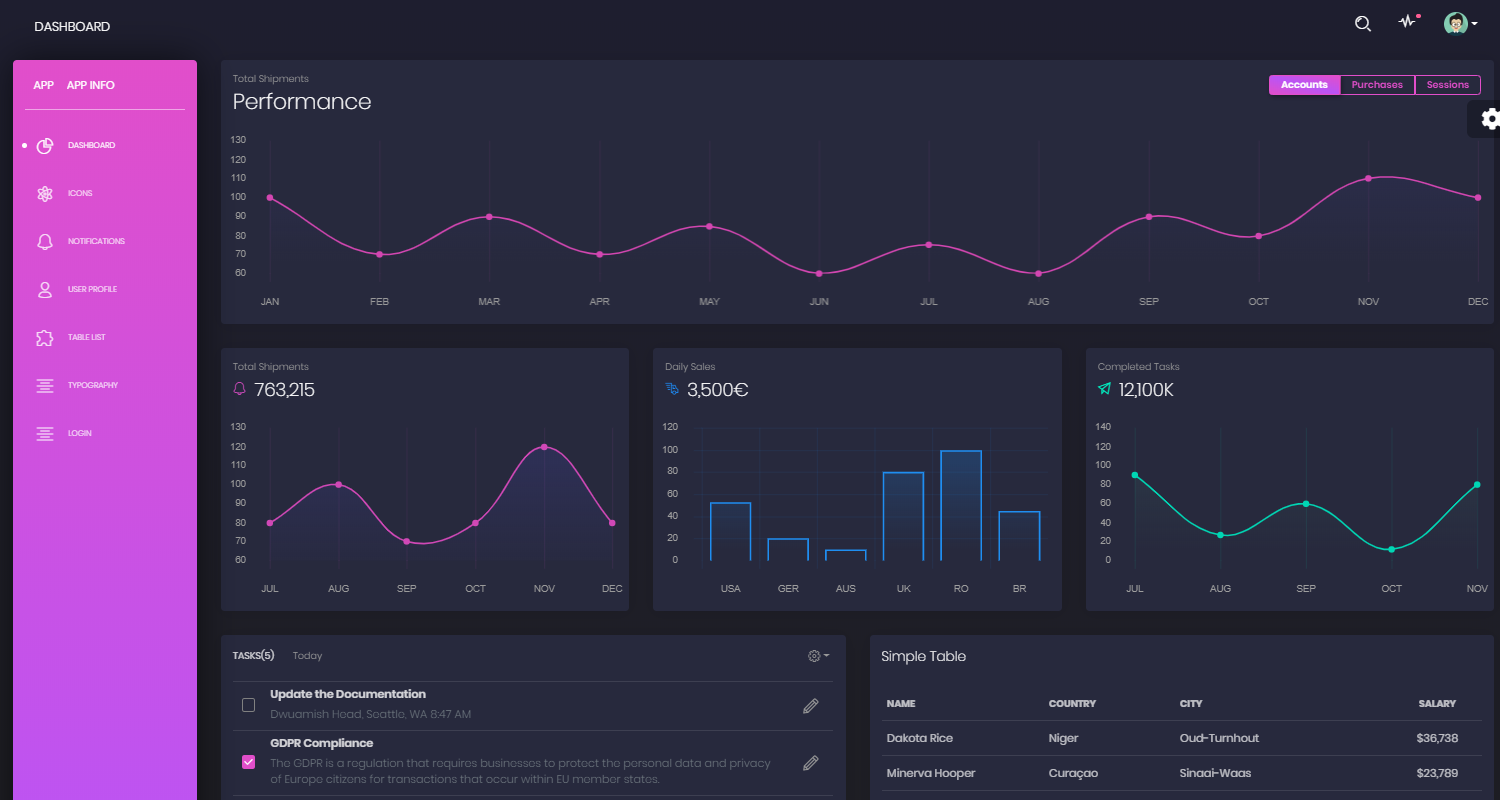
Flask Dashboard Black - Main Dashboard Screen

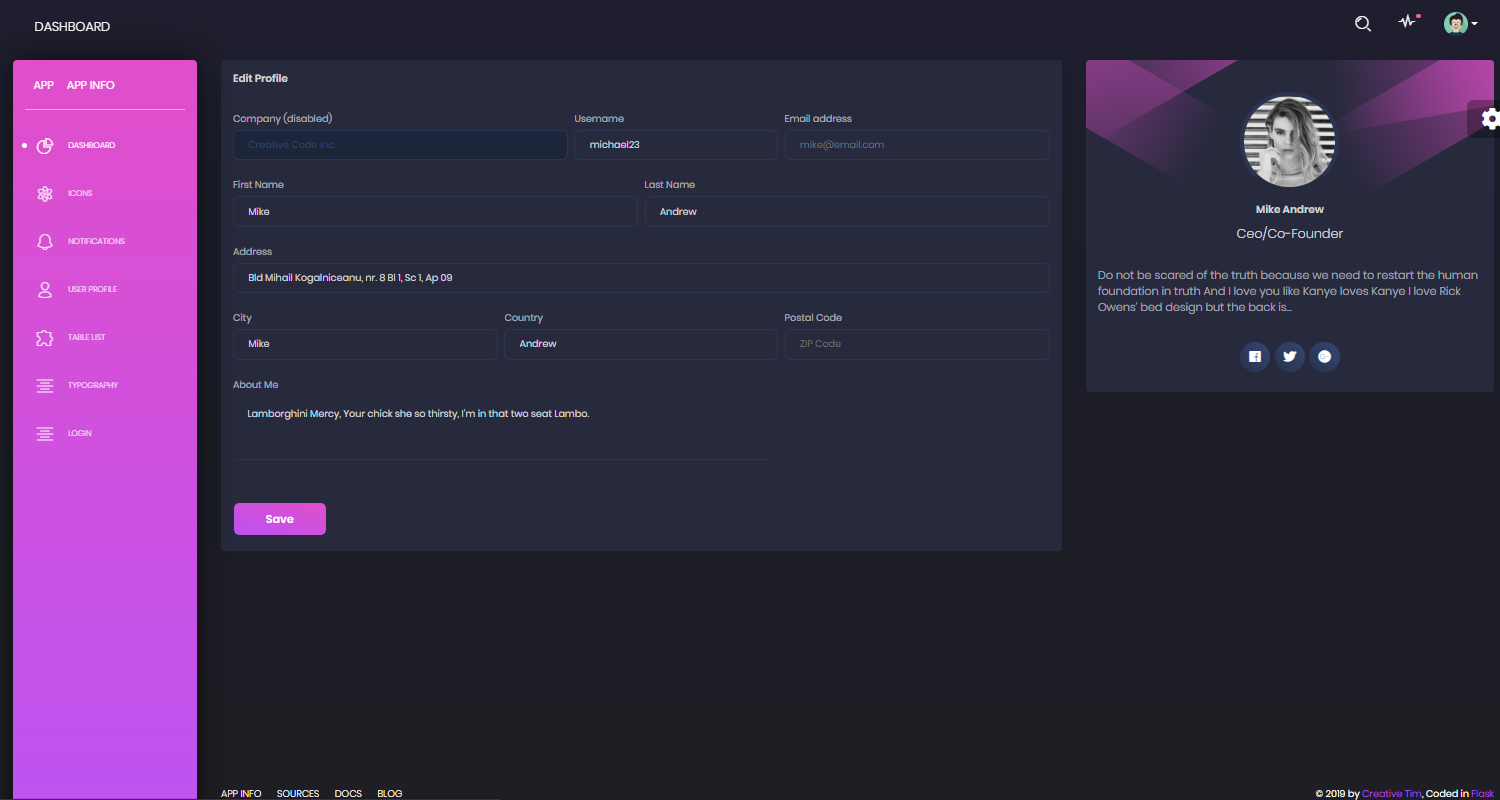
Flask Dashboard Black - User Profile Page
Where to go from here
This free admin dashboard might help developers, especially beginners to code faster a real product with a commercial value. For more open-source and paid flask admin dashboards please access the AppSeed platform or join the AppSeed community on Discord.
Credits & Links
- Open-Source Admin Dashboards - a popular index published on Github
- Learn how to publish your admin dashboard, here on Admin-Dashboards.com.
Thank you for reading this long article! Let me know your thoughts about this article on Twitter and Facebook.